
By convention, most constants are written in all uppercase with underscores to separate words, LIKE_THIS. The Ruby convention is to use underscores to separate words in a multiword method or variable name.

"?", "!" and "=" are the only weird characters allowed as method name suffixes (! or bang labels a method as dangerous-specifically, as the dangerous equivalent of a method with the same name but without the bang. Method names should begin with a lowercase letter (or an underscore). Examples: module MyMath, PI=3.1416, class MyPune. Class names and module names are constants, and follow the constant naming conventions. Ruby defines a number of global variables that include other punctuation characters, such as $_ and $-K.Ī constant name starts with an uppercase letter followed by name characters. A global variable name can be formed using ''$-'' followed by any single character ($counter, $COUNTER, $-x).
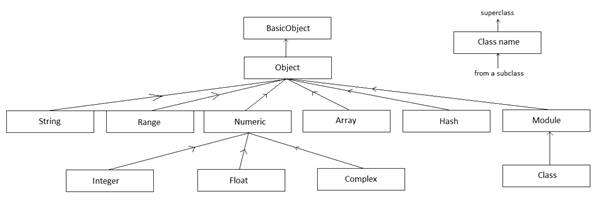
Only one copy of a particular class variable exists for a given class. An instance variable (declared within an object always "belongs to" whatever object self refers to) name starts with an ''at'' sign followed by a name A class variable (declared within a class) name starts with two ''at'' signs followed by a name A class variable is shared among all objects of a class.A local variable (declared within an object) name consists of a lowercase letter (or an underscore) followed by name characters (sunil, _z, hit_and_run).Variable name itself denotes its scope (local, global, instance, etc.). You can use variables in your Ruby programs without any declarations. Variables in Ruby can contain data of any type. A name is an uppercase letter, lowercase letter, or an underscore ("_"), followed by Name characters (this is any combination of upper- and lowercase letters, underscore and digits). Uppercase letter means ''A'' through ''Z,'' and digit means "0" through "9". Lowercase letter means the characters "a" through "z". Certain names, are reserved words and should not be used as variable, method, class, or module name.
The first character of a name helps Ruby to distinguish its intended use. Ruby Names are used to refer to constants, variables, methods, classes, and modules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
